Plant
| Home | Animals | Insects | Mayans | Kid Stuff | Links |
Medicinal Plants
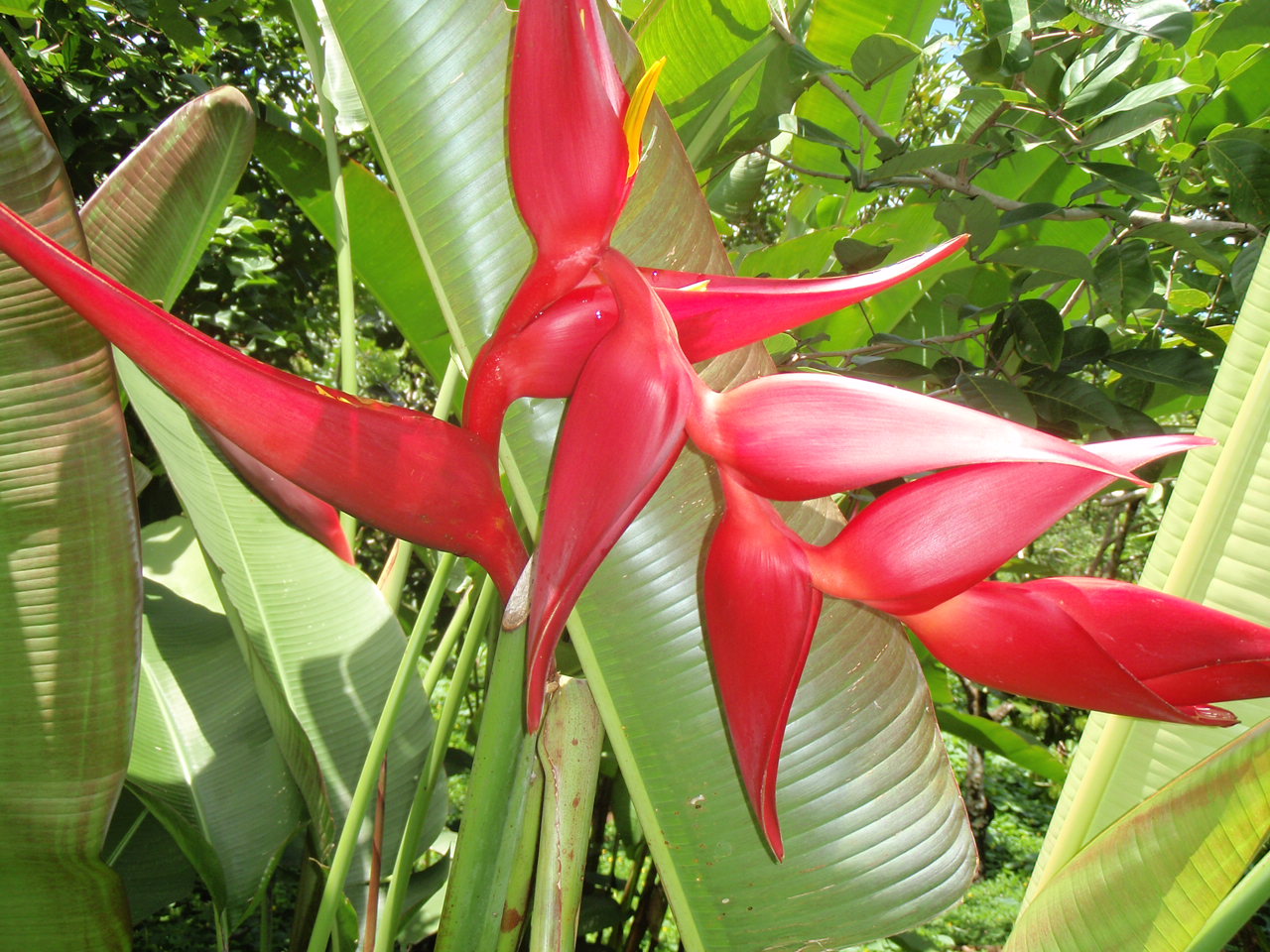
Heliconias
Trees
Bromeliads
Edible Plants
Gingers
Orchids
Aquatic Plants
Miscellaneous Plants
Plants, they are the reason for the rainforest, and the reason the rainforests are disapearing. For this purpose, some of the pages on this section are some of the most intensive and hopefully, informative for you. Guatemala's flora includes more than 8,000 species of plants in 19 different ecosystems ranging from the mangrove wetland forests on both coasts to the pine forests of the mountainous interior and the cloud forests at higher altitudes. However, at this point the plants you will see in this section are primarily ones that you will find in this warm tropical climate of Izabal.
Change in Forest Cover: Between 1990 and 2000, Guatemala lost an average of 54,000 hectares of forest per year. The amounts to an average annual deforestation rate of 1.14%. Between 2000 and 2005, the rate of forest change increased by 12.8% to 1.28% per annum. In total, between 1990 and 2005, Guatemala lost 17.1% of its forest cover, or around 810,000 hectares. Guatemala lost -402,000 hectares—0—of its primary forest cover during that time. Deforestation rates of primary cover have decreased 17.0% since the close of the 1990s. Measuring the total rate of habitat conversion (defined as change in forest area plus change in woodland area minus net plantation expansion) for the 1990-2005 interval, Guatemala lost 14.1% of its forest and woodland habitat and this trend continues today. For more information on Agriculture here click here.
Groups of people have dedicated their lives to try to identify and classify all the plants on earth and it will never be completed. As global warming changes environments, new molds and fungi evolve that cause diseases in the host plants which in turn develop their own immunities so new species evolve. The climate changes also change rainy seasons which alter migrations of birds and insects that feed on predatory insects on plants which are causing major changes in the food chain for various ecosystems. In this section you will also find that many of the plants will cross categories, for example, one tree may have edible fruit that is medicinal.
A NASA research document came to the conclusion that “house plants can purify and rejuvenate air within our houses and workplaces, safeguarding us all from any side effects connected with prevalent toxins such as formaldehyde, ammonia and also benzene.”
Here are the results of the NASA research study:
Common name Scientific name Score 1 Areca palm Chrysalidocarpus lutescens 8.5 2 Lady palm Rhapis excelsa 8.5 3 Bamboo palm Chamaedorea seifrizii 8.4 4 Rubber plant Ficus robusta 8.0 5 Dracaena “Janet Craig” Dracaena deremensis “Janet Craig” 7.8 6 English ivy Hedera helix 7.8 7 Dwarf date palm Phoenix roebelinii 7.8 8 Ficus Alii Ficus macleilandii “Alii” 7.7 9 Boston fern Nephrolepis exalta “Bostoniensis” 7.5 10 Peace lily Spathiphyllum sp. 7.5









