Systemic Reaction
A "systemic
reaction" is different in kind from a local reaction that it is characterised
by symptoms that happen in locations different from that of the sting
because the body is reacting allergically to the venom.
In the two photographs of this unfortunate victim the body has responded to the increased histamine levels by swelling in areas other than the sting site.
The typical mild reactions would includes symptoms such as skin flushing, itchy skin, and headaches whilst more severe reactions would include difficulty in swallowing, chest wheezing, nausea, abdominal cramps, palpitations, faintness and lack of blood pressure. For the very sensitive victim, severe symptoms can present themselves in minutes and without treatment life can be seriously threatened. It is very important to note that once a person has had an allergic reaction to an insect sting (they have become sensitized) then they will probably suffer increasingly difficult symptoms on each subsequent sting.
While these pictures are extreme they are very good illustrations of the cross reactivity.
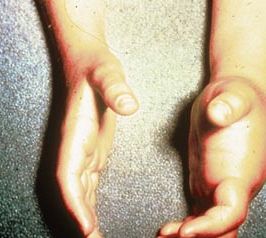
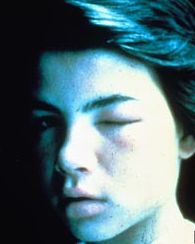




Cross Reactivity
Although the exact mechanism isn't yet understood, allergy sufferers sometimes find that once they have become sensitized to certain allergens, they also exhibit allergic symptoms when exposed to related substances. For example, if you have an allergic reaction to honeybee venom, you might also test positive for hypersensitivity to all other types of bee venom.
The same is true of food groups - very often an allergy to a certain type of pollen or dustborne particle means that the victim may also be allergic to particular foods.