Apple Snail Pomacea flagellata erogata
The Central American apple snails species flagellata is highly variable in shape (see shell photographs below) and over 30 variations have been described as separated species in the past. Nowadays all this species are recognized as one species with 4 subspecies:
Pomacea flagellata flagellata (Say, 1827)
Pomacea flagellata livescens (Reeve, 1856)
Pomacea flagellata erogata (Fisher & Crosse, 1890)
Pomacea flagellata dysoni (Hanley, 1854)Shell:
Pomacea flagellata flagellata:
Colour: Deep olive-green, reddish brown to nearly black; many thin, dark spiral bands, sometimes only faint bands or completely absent, highly variable subspecies .
Relatively thick shell with an ovate shape and relatively flat (over 120 angle) sutures. In some occasions, the sutures are almost absent, resulting in a smooth spire.
The shell lip is often slightly reflected and the umbilicus is narrow and deep.
Size: 53-60 mm wide, 55-62 mm high (only slightly higher then wide).
There are many variations known of this subspecies, mainly variations in the suture angle.
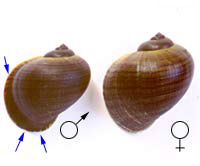
One of the most stricking features of this snail is the difference between males and females: while in many apple snail species, the male has a rounder and wider shell opening (probably to host its large penial complex), Pomacea flagellata flagellata goes beyond that. The growth of the male ceases at a certain point and the lip of the shell grows outwards, creating a large aperture, trumpet like appearance.
Flagellata flagellata, shell from underside.
Flagellata flagellata, shell from above (from Balneario, Teuchitlan, Mexico).
Flagellata flagellata.
Flagellata flagellata in the aquarium.
Pomacea flagellata livescens:
One of the largest subspecies: 66-88 mm wide, 95-102 mm high. The shell has globular shape, often as high as width (in the smaller shells). The sutures are more indented compared with flagellata flagellata subspecies (less than 120), giving this species a more shouldered shell shape.Pomacea flagellata erogata:
This dwarf subspecies is highly variable in size (28-36 mm wide, 30-40 mm high) and can mature at almost any size. Specimens of about 2 cm in height have been seen in copulation. The shell surface of this sub species is often erroded.
Colour: dark olive with series of reddish brown bands which are often visible within the aperture.
Pomacea flagellata erogata inhabits swamps and temporary ponds, whereas the ofther subspecies rather inhabit canals, lakes and rivers.
Flagellata erogata, shell from underside.
Flagellata erogata, shell, back view.
Live specimen (from Palenque, Mexico), subspecies erogata (Fisher & Crosse, 1890).
(picture not licenced under creative commons)
Pomacea flagellata dysoni:
Not much is known from this rare subspecies.
The strong shell is globular in shape and has a highly polished and malleated (hammered) surface.
Colour: reddish-grey; small dark spiral bands close to the umbilicus; aperture: yellow at the top to orange at the bottom.Operculum (of all subspecies): relatively big, dark and thick; narrow at the top.
Body: Pale grey to dark foot, with black pigmented spots on the upper side of the body, sometimes almost completely black at the back of the food and the in the head.Eggs: Very condensed (packed together without leaving air spaces between the eggs); pale orange colour.
Sex differences in adult Pomacea flagellata flagellata snails.
The female is larger and has a straight shell opening, while the male (left) has a extended shell lip.
Pomacea flagellata eggs at 15 days, 2 days before they hatched.
Note the dark colour of the fertile eggs.
Pomacea flagellata eggs after hatching. Only a few eggs did not hatch and some little snails did not manage to get out in time and died.Food: Yes, they are edible and great if you like escargout but you are probable more interested in their eating habits. These snails eat all types of plants (including Java fern) in huge amounts at fast speed. In deficiency of food, this species can even act like predators on other snails and even cannibalism has been observed in total absense of food. Not suited for planted aquaria.
Behaviour: amphibious animal; submerged during the day, hidden in the vegetation near the border and the surface or buried in the mud. More active during the night, also leaves the water in search for fresh vegetation.
Distribution:
Pomacea flagellata flagellata: central Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panama and Colombia (Magdalena drainage area).
Pomacea flagellata livescens: Mexico (Tabasco and Chiapas) and north-east Guatemala (Pten Lake).
Pomacea flagellata erogata: similar distribution as flagellata flagellata, inhabits swamps and temporary ponds.
Pomacea flagellata dysoni: Honduras.