|
|




|
Family: Arecaceae
Genus: Cocos
Species: C. nucifera
Common Names: Chocolate, cacao, criollo, cacaoyer, kakao
Parts Used: Fruit, Seed, juice, Leaves
| PLANT DESCRIPTION | Documented Properties
& Actions: | Antiseptic, antifungal, antibiotic, diuretic, emmenagogueue, parasiticide, vulnerary
| Plant
Chemicals
Include:
|
Acetic-acid, aesculetin, alanine, alkaloids, alpha-sitosterol, alpha-theosterol, amyl-acetate, amyl-alcohol, amyl-butyrate, amylase, apigenin-7-o-glucoside, arabinose, arachidic-acid, arginine, ascorbic-acid, ascorbic-acid-oxidase, aspariginase, beta-carotene, beta-sitosterol, beta-theosterol, biotin, caffeic-acid, caffeine, calcium, campesterol, catalase, catechins, catechol, cellulase, cellulose, chlorogenic-acid, chrysoeriol-7-o-glucoside, citric-acid, coumarin, cyanidin, cyanidin-3-beta-l-arabinoside, cyanidin-3-galactoside, cyanidin-glycoside, cycloartanol, d-galactose, decarboxylase, dextrinase, diacetyl, dopamine, epigallocatechin, ergosterol, ferulic-acid, formic-acid, fructose, furfurol, galacturonic-acid, gallocatechin, gentisic-acid, glucose, glutamic-acid, glycerin, glycerophosphatase, glycine, glycolic-acid, glycosidase, haematin, histidine, i-butyric-acid, idaein, invertase, isobutylacetate, isoleucine, isopropyl-acetate, isovitexin, kaempferol, l-epicatechin, leucine, leucocyanidins, linalool, linoleic-acid, lipase, luteolin, luteolin-7-o-glucoside, lysine, lysophosphatidyl-choline, maleic-acid, mannan, manninotriose, mannose, melibiose, mesoinositol, methylheptenone, n-butylacetate, n-nonacosane, niacin, nicotinamide, nicotinic- acid, nitrogen, nonanoic-acid, o-hydroxyphenylacetic-acid, octoic-acid, oleic- acid, oleo-dipalmatin, oleopalmitostearin, oxalic-acid, p-anisic-acid, p-coumaric-acid, p-coumarylquinic-acid, p-hydroxybenzoic-acid, p-hydroxyphenylacetic-acid, palmitic-acid, palmitodiolen, pantothenic-acid, pectin, pentose, peroxidase, phenylacetic-acid, phenylalanine, phlobaphene, phosphatidyl-choline, phosphatidyl- ethanolamine, phosphatidyl-inositol, phospholipids, phosphorus, phytase, planteose, polygalacturonate, polyphenol-oxidase, polyphenols, proline, propionic-acid, propyl-acetate, protocatechuic-acid, purine, pyridoxine, quercetin, quercetin-3-o-galactoside, quercetin-3-o-glucoside, quercitrin, raffinase, raffinose, reductase, rhamnose, riboflavin, rutin, rutoside, saccharose, salsolinol, serine, sinapic-acid, stachyose, stearic-acid, stearodiolein, stigmasterol, sucrose, syringic-acid, tannins, tartaric-acid, theobromine, theophylline, thiamin, threonine, trigonelline, tyramine, tyrosine, valerianic-acid, valine, vanillic-acid, verbascose, verbascotetrose, vitexin
|
Coconut - Medicinal Properties
Modern medical science is now confirming the use of coconut (Cocos nucifera) in treating
many of the following conditions. Published studies in medical journals show
that coconut, in one form or another, may provide a wide range of health
benefits. Some of these are summarized below:
-
Kills viruses that cause influenza, herpes, measles, hepatitis C,
SARS, AIDS, and other illnesses.
-
Kills bacteria that cause ulcers, throat infections, urinary tract
infections, gum disease and cavities, pneumonia, and gonorrhea, and
other diseases.
-
Kills fungi and yeasts that cause candidiasis, ringworm, athlete's
foot, thrush, diaper rash, and other infections.
-
Expels or kills tapeworms, lice, giardia, and other parasites.
-
Provides a nutritional source of quick energy.
-
Boosts energy and endurance, enhancing physical and athletic
performance.
-
Improves digestion and absorption of other nutrients including
vitamins, minerals, and amino acids.
-
Improves insulin secretion and utilization of blood glucose.
-
Relieves stress on pancreas and enzyme systems of the body.
-
Reduces symptoms associated with pancreatitis.
-
Helps relieve symptoms and reduce health risks associated with
diabetes.
-
Reduces problems associated with malabsorption syndrome and cystic
fibrosis.
-
Improves calcium and magnesium absorption and supports the
development of strong bones and teeth.
-
Helps protect against osteoporosis.
-
Helps relieve symptoms associated with gallbladder disease.
-
Relieves symptoms associated with Crohn's disease, ulcerative
colitis, and stomach ulcers.
-
Improves digestion and bowel function.
-
Relieves pain and irritation caused by hemorrhoids.
-
Reduces inflammation.
-
Supports tissue healing and repair.
-
Supports and aids immune system function.
-
Helps protect the body from breast, colon, and other cancers.
-
Is heart healthy; improves cholesterol ratio reducing risk of
heart disease.
-
Protects arteries from injury that causes atherosclerosis and thus
protects against heart disease.
-
Helps prevent periodontal disease and tooth decay.
-
Functions as a protective antioxidant.
-
Helps to protect the body from harmful free radicals that promote
premature aging and degenerative disease.
-
Does not deplete the body's antioxidant reserves like other oils
do.
-
Improves utilization of essential fatty acids and protects them
from oxidation.
-
Helps relieve symptoms associated with chronic fatigue syndrome.
-
Relieves symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia
(prostate enlargement).
-
Reduces epileptic seizures.
-
Helps protect against kidney disease and bladder infections.
-
Dissolves kidney stones.
-
Helps prevent liver disease.
-
Is lower in calories than all other fats.
-
Supports thyroid function.
-
Promotes loss of excess weight by increasing metabolic rate.
-
Is utilized by the body to produce energy in preference to being
stored as body fat like other dietary fats.
-
Helps prevent obesity and overweight problems.
-
Applied topically helps to form a chemical barrier on the skin to
ward of infection.
-
Reduces symptoms associated the psoriasis, eczema, and dermatitis.
-
Supports the natural chemical balance of the skin.
-
Softens skin and helps relieve dryness and flaking.
-
Prevents wrinkles, sagging skin, and age spots.
-
Promotes healthy looking hair and complexion.
-
Provides protection form damaging effects of ultraviolet radiation
form the sun.
-
Helps control dandruff.
-
Does not form harmful by-products when heated to normal cooking
temperature like other vegetable oils do.
-
Has no harmful or discomforting side effects.
-
Is completely non-toxic to humans.
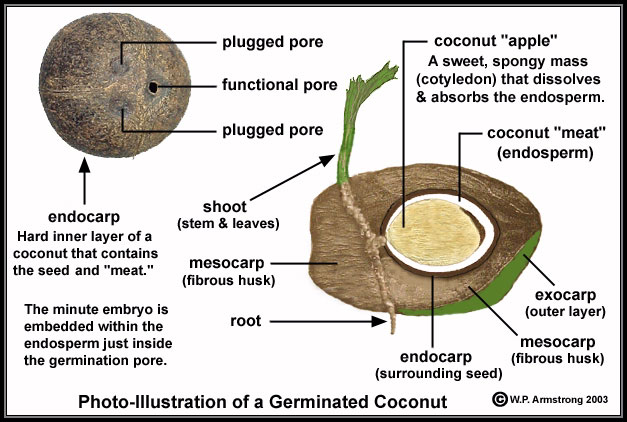
Botanically, a coconut is a simple dry fruit known as a fibrous drupe (not a true nut). The husk (mesocarp) is composed of fibres called coir and there is an inner "stone" (the endocarp). This hard endocarp (the coconut as sold in the shops of non-tropical countries) has three germination pores that are clearly visible on the outside surface once the husk is removed. It is through one of these that the radicle emerges when the embryo germinates. Adhering inside wall of endocarp is the testa with a thick albuminous endosperm, the coconut meat, the white and fleshy edible part of the seed.
When viewed on end, the endocarp and germination pores resemble the face of a monkey, the Portuguese word for which is macaco, sometimes abbreviated to coco, whence the name of the fruit. The specific name nucifera is Latin for nut bearing.
When the coconut is still green, the endosperm inside is thin and tender, a favourite snack. But the main reason to pick the nut at that stage is to drink its juice; a big nut contains up to one litre of refreshing drink. When the nut has ripened and the outer husk has turned brown, a couple of months later, it will fall from the tree of its own accord. At that time the endosperm has thickened and hardened, while the juice has become somewhat bitter.
Source, History, and Preparation. The origin of this plant are the subject of controversy with some authorities claiming it is native to southeast Asia, while others claim its origin is in northwestern South America. Fossil records from New Zealand indicate that small, coconut-like plants grew there as far back 15 million years ago. Even older fossils have been uncovered in Rajasthan & Maharashtra, India. Regardless of its origin, the coconut has spread across much of the tropics, probably aided in many cases by sea-faring peoples. The fruit is light and buoyant and presumably spread significant distances by marine currents: fruits collected from the sea as far north as Norway have been found to be viable (subsequently germinated under the right conditions). In the Hawaiian Islands, the coconut is regarded as a Polynesian introduction, first brought to the Islands by early Polynesian voyagers from their homelands in the South Pacific.
Coconut - traditional medicine
Multipurpose plants in the true sense, coconut palms have been used to treat an extraordinary range of health problems. The seeds, roots and even flowers have been prepared into pastes, infusions and creams for Ayurvedic and other traditional South Asian medicines.
White meat and water from the cavity are used for heart conditions, dysentery, fever, pain, digestive and bladder problems, to quench thirst and as an aphrodisiac. To treat diarrhoea, meat from young fruits is mixed with other ingredients and rubbed onto the stomach. Oil prepared from boiling coconut milk is thought of as antiseptic and soothing and so is smoothed onto the skin to treat burns, ringworm and itching. These two properties are also valued in Western medicine. It has been applied to the scalp in the belief that it might encourage hair growth and prevent grey hair.
Other parts of the palm are also used in traditional South Asian medicine. Juice tapped from flowers stalks is given to cure fever and promote urination. Fresh juice mixed and heated together with rice flour is applied to gangrenous ulcers and skin boils, while fermented juice is taken as a laxative. The roots have been used for a host of ailments, including as an infusion for sore throat gargles. Coconut palm hearts are nourishing and are regarded as good for the digestion. To regulate menstruation, a paste made from grinding the hearts with molasses is eaten every day for several successive days. The fresh juices from the hearts are used against fevers.
Coconuts also feature in traditional medicines in other parts of the world. In Indo-China, the seeds are used as a treatment for skin and nasal ulcers.
|
ETHNOBOTANY: WORLDWIDE USES
|
| Dominican Republic |
Diuretic, Kidney |
| Elsewhere |
Antiseptic, Burn, Emmenagogueue, Eye, Liqueur, Parturition, Wound |
| Ghana |
Cough, Dentifrice |
| Haiti |
Burn, Dry-Lip , Rheumatism |
| Japan |
Suppository-Base |
| La |
Coffee, Liqueur |
| Mexico |
Bite(Snake), Wound |
| Panama |
Antiseptic, Eye, Listlessness, Parasiticide, Pregnancy |
| Venezuela |
Alopecia, Pilatory |


|
|